MachPro Commands, Function Buttons, and Dashboard
Commands
The system has many packaged functions called commands. These commands can perform a variety of actions, such as turning on the spindle or zeroing an axis. All commands have an action associated with them. Some actions also have a feedback associated with them, such as the 'Spindle Forward' command where the feedback is whether the spindle is currently running forward or not.
Commands and User Commands can be assigned to function buttons on the control, in order to customize the experience.
User Commands
Additionally custom commands, called User Commands, can be configured in the 'Screen Configuration' dialog. This is accessible through the 'Screen Config' button on the Service/Maintenance tab.
To make a new User Command, press the 'Add' button. Each User Command should have a unique name. To edit a User Command, select its name from the list. A searchable list of actions for the command is available in the first box. This selects the general type of action to be done. The second box, labeled 'Options', is also part of the action and must be selected.
The 'Feedback Source' and 'Feedback Target' sections are optional. They are relevant if the User Command will be assigned to a function button. Some User Commands won't have a logical feedback source. A reasonable example is for a command that turns soft limits on and off: the feedback would be if soft limits is on or off. The feedback target offers a way to do a simple forwarding of the user command state if desired.
One option for user commands are User Scripts. These are lua functions that will be executed as the command, to get the feedback state, or to forward to the target. This is a way to create completely custom functionality. They should always be done in the UserGUIModule.UserStartUpScript function. The following is an example of how to create these lua function in the UserGUIModule.
function UserGUIModule.UserStartUpScript()
local action_func = function()
local state = w.GetSignalState(mc.OSIG_OUTPUT0)
w.SetSignalState(mc.OSIG_OUTPUT0, not state)
end
w.CreateUserCommandActionOption("Toggle Output #0", action_func)
local feedback_func = function()
return w.GetSignalState(mc.OSIG_OUTPUT0)
end
w.CreateUserCommandFeedbackOption("Output #0", feedback_func)
return true, true, w.FunctionCompleted()
endHardware Function Buttons
The MachPro operator panels and wireless pendants have a number of function buttons on them, labelled F1, F2, etc. These buttons initially do nothing, but can have commands or user commands mapped to them. This is done through the MachMotion operator panel configuration.
Upon saving and exiting configuration, these commands will be mapped to the function buttons.
On the screen, there are five function buttons underneath the axis DROs. Instructions on how to configure those buttons, as well as how to add more function buttons to the screen, are in the Dashboard section.
Dashboard
 The MachPro controls have multiple places to customize the interface to meet the users needs. The operator panel has function buttons that can be assigned operations, and there are two dashboards on the screen for the user to place widgets that they want to see. One dashboard is on the far right of the control and is available from all views. The other dashboard available to customize is on the service page.
The MachPro controls have multiple places to customize the interface to meet the users needs. The operator panel has function buttons that can be assigned operations, and there are two dashboards on the screen for the user to place widgets that they want to see. One dashboard is on the far right of the control and is available from all views. The other dashboard available to customize is on the service page.
Dashboards can be configured by right-clicking on them to access their menu. The user can choose how many and which widgets to show on the dashboard, as well as their layout. There is a wide variety of widgets to select from, and some widgets have additional options within them accessible through the 'Configure Widget' menu option.
Software Function Buttons
One particular widget is the 'Function Buttons' widget. It is configurable in a similar way to the overall dashboard, but instead of selecting widgets, the user can select Commands to run on press and release. The user can also set the labels and colors of the button to suit them.
MDI commands
Aside from running Commands, function buttons can be configured to run an MDI command instead. Setting the MDI command to run, either press or release, is accessible through the right-click menu. Those menu options will only be available if the button does not have a Command set for it already. To create a multiline MDI command add a "\n" between the MDI lines.
For example, to run this command:
M6 T1
M3 S1000You must program it like this: M6 T1 \n M3 S1000
The \n combination is used in many contexts to insert a new line.
Button press, release, toggle
Usually we only configure the button press, but we can also configure the button release function. Functions that toggle have a similar effect to the press and release functions.
Configurable Dashboards
Most controls have at least three dashboards on the screen, the first one is under the Axis Positions (Labeled '1' in the example below) referred to as the Axis Positions Dashboard, and the second on the right side of the screen referred to as the Side Bar Dashboard (Labeled '2' in the example below). The third dashboard is on the Service page.
Axis Positions Dashboard
The Axis Position Dashboard is locked to only allow the Function Button widget with 5 configurable buttons. These buttons configurable in the same manner as the function button widget on the Side Bar Dashboard, through the right-click menu.
Side Bar Dashboard
On the right side of the screen is a large Dashboard with lots of space to add Widgets that will improve productivity. Configure the dashboard through the right-click menu.
Software Function Button Commands and Descriptions
| Command | Description |
| Block Delete Toggle | When enabled, skips G-code lines beginning with a forward slash (/) during program execution. |
| Clear Scheduler 0 | Clears the pending file queue in the Scheduler for instance 0 on a multi‑instance system. |
| Clear Tool Change State | Resets any in‑progress tool change state back to idle, clearing interlocks or prompts. |
| Close CNC Software | Closes and exits the MachMotion CNC software environment safely. |
| Close GCode | Closes the currently loaded G‑code file without quitting the control software. |
| Compile Scripts | Recompiles .mcs scripts after Mach core configuration changes, ensuring updated logic is active. |
| Convert Screen To Multi Instance | Converts the current screen/profile to support multiple Mach instances on one PC. |
| Cut Recovery | Resumes a program after interruption, re‑establishing position and conditions for safe continuation. |
| Cutter Compensation Type A Toggle | Toggles cutter compensation Type A mode as defined in cutter comp documentation. |
| Cutter Compensation Type B Toggle | Toggles cutter compensation Type B mode as defined in cutter comp documentation. |
| Cutter Compensation Type C Toggle | Toggles cutter compensation Type C mode as defined in cutter comp documentation. |
| Cycle Start | Starts execution of the loaded program; same function as the panel Cycle Start. |
| Cycle Start 0 | Starts execution of the loaded program for instance 0 in a multi‑instance setup. |
| Cycle Stop | Stops the running program or commanded motion; same as the panel Cycle Stop. |
| Cycle Stop 0 | Stops the running program or motion on instance 0 only. |
| DeReference All | Clears referenced (homed) status for all axes on the active instance. |
| DeReference All Instances | Clears referenced (homed) status for all axes across all instances. |
| DeReference X | Clears referenced (homed) status for the X axis. |
| DeReference Y | Clears referenced (homed) status for the Y axis. |
| DeReference Z | Clears referenced (homed) status for the Z axis. |
| Disable | Disables machine motion drives/interlocks system‑wide; machine cannot move. |
| Dry Run To Line | Processes G‑code without coolants to a selected line, helpful for verification. |
| Dry Run Toggle | Toggles dry‑run mode to process code without spindle, mist, or flood outputs. |
| Edit GCode | Opens the loaded G‑code in the editor for quick changes. |
| Edit Offsets Off | Locks offsets to prevent editing in the offsets page. |
| Edit Offsets On | Unlocks offsets, allowing editing of fixture and tool offsets. |
| Edit Offsets Toggle | Toggles between locked and unlocked offset editing states. |
| Edit Scheduler 0 | Opens the Scheduler editor for instance 0 in a multi‑instance system. |
| Enable | Enables machine motion, allowing jogging and program execution. |
| Enable Reset | Enables and arms the Reset system to clear faults and rewind modals. |
| Enable Reset 0 | Arms the Reset system only for instance 0. |
| Enable Scheduler 0 | Enables the Scheduler service for instance 0 so queued jobs can run. |
| Enable Toggle | Toggles machine enable/disable state. |
| Enable X Axis Toggle | Toggles enable state of the X axis servo/drive. |
| Enable Y Axis Toggle | Toggles enable state of the Y axis servo/drive. |
| Enable Z Axis Toggle | Toggles enable state of the Z axis servo/drive. |
| Feed Hold | Pauses program motion and enters hold; can resume with Cycle Start. |
| Feed Hold 0 | Pauses motion for instance 0 only; resume with Cycle Start 0. |
| Feed Hold Retract | Retracts along a safe vector while entering feed hold to clear the part. |
| Feed Hold Retract 0 | Retracts and holds on instance 0 only. |
| Feedrate Override Decrement | Decreases commanded feedrate override in preset steps. |
| Feedrate Override Increment | Increases commanded feedrate override in preset steps. |
| Feedrate Override Reset | Resets feedrate override to 100% (nominal programmed feed). |
| File Resume | Resumes execution of a previously paused or interrupted file. |
| Find Tool Changes | Scans the loaded G‑code and highlights M6 tool change locations. |
| Flood Toggle | Turns flood coolant on or off. |
| GCAdapter Adapt Folder | Processes all files in a folder with the G‑code Adapter per configured rules. |
| GCAdapter Adapt Folder Showing Toolpaths | Adapts a folder and displays resulting toolpaths for review. |
| GCAdapter Adapt GCode | Runs G‑code Adapter on the current file to apply post/cleanup rules. |
| GCAdapter Settings | Opens the G‑code Adapter settings dialog for configuration. |
| GCode CNTL 1 MST Toggle | Toggles M/S/T lock behavior for GCode Control 1 (mist, spindle, tool). |
| GCode File Repeat Off | Disables automatic repeating of the loaded G‑code file. |
| GCode File Repeat On | Enables automatic repeating of the loaded G‑code file. |
| GCode File Repeat Toggle | Toggles the file repeat setting for the loaded program. |
| GCode Shortcut1 | Executes user‑assigned shortcut action 1 for G‑code operations. |
| GCode Shortcut2 | Executes user‑assigned shortcut action 2 for G‑code operations. |
| GCode Shortcut3 | Executes user‑assigned shortcut action 3 for G‑code operations. |
| Goto Machine Zero | Moves to machine coordinate zero (G53 origin) using a safe move. |
| Goto Part Zero | Moves to current work offset origin (e.g., G54 X0 Y0 Z0) safely. |
| Goto Positions Selection | Moves to a position selected from predefined positions list. |
| Goto Tool Change | Moves to the defined tool change position for manual or automatic changes. |
| Home All | Homes all axes on the active instance. |
| Home All 0 | Homes all axes on instance 0. |
| Home All Dereferenced Axes | Homes only axes currently not referenced (not homed). |
| Home All Selected Instance | Homes all axes on the currently selected instance in multi‑instance systems. |
| Home X | Homes the X axis using its home switch routine. |
| Home Y | Homes the Y axis using its home switch routine. |
| Home Z | Homes the Z axis using its home switch routine. |
| Inhibit Jogging When Not Homed Toggle | Prevents jogging until the machine has been homed; safety interlock. |
| Inhibit X Jogging Toggle | Enables or disables jogging on the X axis. |
| Inhibit Y Jogging Toggle | Enables or disables jogging on the Y axis. |
| Inhibit Z Jogging Toggle | Enables or disables jogging on the Z axis. |
| Interrupt | Triggers an immediate program interrupt for safe attention or intervention. |
| Jog Tool Magazine To Next Pocket | Jog the tool magazine to the next pocket position. |
| Jog Tool Magazine To Next Pocket 2 | Jog tool magazine 2 to its next pocket position. |
| Jog Tool Magazine To Next Pocket 3 | Jog tool magazine 3 to its next pocket position. |
| Jog Tool Magazine To Next Pocket 4 | Jog tool magazine 4 to its next pocket position. |
| Jog Tool Magazine To Previous Pocket | Jog the tool magazine to the previous pocket position. |
| Jog Tool Magazine To Previous Pocket 2 | Jog tool magazine 2 to its previous pocket position. |
| Jog Tool Magazine To Previous Pocket 3 | Jog tool magazine 3 to its previous pocket position. |
| Jog Tool Magazine To Previous Pocket 4 | Jog tool magazine 4 to its previous pocket position. |
| Laser Pointer Toggle | Turns the laser pointer alignment aid on or off. |
| Limit Override Toggle | Temporarily overrides software limits; use with caution. |
| Load GCode | Opens a file dialog to load a G‑code program into memory. |
| Manual Mode Toggle | Switches between automatic run and manual (MDI/jog) control modes. |
| Mist Toggle | Turns mist coolant on or off. |
| MST Lock Toggle | Toggles lock that prevents Macro, Spindle, and Tool actions. |
| Next Pocket | Advance the currently selected tool magazine to the next pocket. |
| Next Tool | Selects the next tool number in the tool table or changer sequence. |
| OP Zone App QR Code | Displays the Operation Zone app QR code for quick access on mobile devices. |
| Open Commands Dialog | Opens a dialog to issue predefined command macros or actions. |
| Open GCode Nesting | Opens the G‑code nesting utility to arrange multiple parts. |
| Open Global Message Config | Opens configuration for global on‑screen messages and alerts. |
| Open Machine Calibration | Opens the machine calibration hub. |
| Open Machine Calibration Automatic Config | Opens automatic calibration configuration for probes, setters, or routines. |
| Open Machine Calibration Manual Config | Opens manual calibration configuration workflows. |
| Open Machine Calibration Screw Mapping | Opens leadscrew mapping/backlash compensation calibration. |
| Open MachMotion Config | Opens the MachMotion plugin configuration utility. |
| Open MachMotion Modbus Config | Opens Modbus configuration for I/O and device mapping. |
| Open MDI | Opens the MDI input to execute single lines of G‑code. |
| Open Setup Wizard | Launches the guided setup wizard for machine configuration. |
| Optional Stop Off | Turns off M1 optional stop handling within programs. |
| Optional Stop On | Turns on M1 optional stop handling within programs. |
| Optional Stop Toggle | Toggles the M1 optional stop behavior. |
| Park Tool | Parks the current tool at a defined safe location. |
| Part Counters | Opens part counter utilities to view and reset production counts. |
| Plate Alignment | Opens plate alignment routine to square and set workpiece orientation. |
| PLC Sequence Diagnostics | Opens PLC diagnostics to monitor and test sequence logic. |
| Power Off | Shuts down control power with normal delays and interlocks. |
| Power Off Immediate | Immediately shuts down control power, bypassing delays; emergency use. |
| Previous Pocket | Move the tool magazine to the previous pocket. |
| Previous Tool | Selects the previous tool number in the tool table or changer sequence. |
| Recent GCode | Opens a list of recently run G‑code files for quick selection. |
| Refresh Enabled Buttons | Refreshes button enable/disable states based on current machine conditions. |
| Regen ToolPath | Regenerates the toolpath display after edits or reloads. |
| Register Tools | Opens tool pocket registration to map tool numbers to tool pockets |
| Remote Support | Starts a remote support session with MachMotion. |
| Reset | Rewinds the G‑code and resets modal states; clears certain faults. |
| Reset 0 | Performs reset/reload actions for instance 0 only. |
| Reset GCode CNTL 1 MST | Resets M/S/T lock state for GCode Control 1 to defaults. |
| Rewind | Rewinds the current program to its beginning. |
| Rewind 0 | Rewinds the current program to the beginning for instance 0. |
| Run Lua Script | Runs a selected Lua script within the control environment. |
| Save Fixture Offsets | Saves current fixture/work offsets to persistent storage. |
| Screen Profiling For 60 Seconds | Runs performance profiling for 60 seconds and records results. |
| Screen Profiling Toggle | Starts or stops screen performance profiling. |
| Search GCode | Opens search to find text or line numbers within the loaded G‑code. |
| Selected Spindle 1 | Selects spindle 1 as the active spindle for commands. |
| Selected Spindle 2 | Selects spindle 2 as the active spindle for commands. |
| Selected Spindle 3 | Selects spindle 3 as the active spindle for commands. |
| Selected Spindle 4 | Selects spindle 4 as the active spindle for commands. |
| Set GCode CNTL 1 MST | Applies M/S/T lock mode for GCode Control 1 per settings. |
| Set Selected Instance 0 | Sets instance 0 as the active target instance. |
| Single Block Off | Disables single‑block mode; program runs continuously. |
| Single Block On | Enables single‑block mode to execute one block per Cycle Start. |
| Single Block Toggle | Toggles single‑block mode on or off. |
| Skip Spindle Warm Up | Skips the spindle warm‑up routine if scheduled. |
| Soft Limits Off | Disables software travel limits for all axes. |
| Soft Limits On | Enables software travel limits for all axes. |
| Soft Limits Toggle | Toggles software travel limits on or off. |
| Spindle Brake Off | Releases the spindle brake. |
| Spindle Brake On | Applies the spindle brake. |
| Spindle Brake Toggle | Toggles spindle brake between on and off states. |
| Spindle Forward | Starts spindle rotating forward (M3 equivalent). |
| Spindle Forward Toggle | Toggles spindle forward state. |
| Spindle Orient | Orients spindle to a programmed angle for tool change or probing. |
| Spindle Orient Toggle | Toggles spindle orient function on or off. |
| Spindle Override Decrement | Decreases spindle speed override in preset steps. |
| Spindle Override Increment | Increases spindle speed override in preset steps. |
| Spindle Override Reset | Resets spindle speed override to 100%. |
| Spindle Range 00 | Selects spindle gear/range 00. |
| Spindle Range 01 | Selects spindle gear/range 01. |
| Spindle Range 02 | Selects spindle gear/range 02. |
| Spindle Range 03 | Selects spindle gear/range 03. |
| Spindle Range 04 | Selects spindle gear/range 04. |
| Spindle Range 05 | Selects spindle gear/range 05. |
| Spindle Range 06 | Selects spindle gear/range 06. |
| Spindle Range 07 | Selects spindle gear/range 07. |
| Spindle Range 08 | Selects spindle gear/range 08. |
| Spindle Range 09 | Selects spindle gear/range 09. |
| Spindle Range 10 | Selects spindle gear/range 10. |
| Spindle Range 11 | Selects spindle gear/range 11. |
| Spindle Range 12 | Selects spindle gear/range 12. |
| Spindle Range 13 | Selects spindle gear/range 13. |
| Spindle Range 14 | Selects spindle gear/range 14. |
| Spindle Range 15 | Selects spindle gear/range 15. |
| Spindle Range 16 | Selects spindle gear/range 16. |
| Spindle Range 17 | Selects spindle gear/range 17. |
| Spindle Range 18 | Selects spindle gear/range 18. |
| Spindle Range 19 | Selects spindle gear/range 19. |
| Spindle Reverse | Starts spindle rotating in reverse (M4 equivalent). |
| Spindle Reverse Toggle | Toggles spindle reverse state. |
| Spindle Speed Variation Toggle | Toggles speed variation function for spindle conditioning or testing. |
| Spindle Stop | Stops the spindle (M5 equivalent). |
| Start Spindle Warm Up | Starts the spindle warm‑up cycle with programmed steps. |
| Step Into Subs | Enables stepping into subroutines during single‑block debugging. |
| Step Into Subs Toggle | Toggles step‑into‑subroutine behavior. |
| Step Over Subs | Steps over subroutines, executing them without entering during debug. |
| Support | Opens MachMotion support resources or contact launcher. |
| Teach Laser Pointer Offsets | Captures laser pointer offset to spindle for alignment/positioning. |
| Teach WorkShift X Offset | Sets current X as workshift offset for the active fixture. |
| Teach WorkShift Y Offset | Sets current Y as workshift offset for the active fixture. |
| Teach WorkShift Z Offset | Sets current Z as workshift offset for the active fixture. |
| Toggle Coordinates View | Toggles displayed coordinates between machine and part views. |
| Tool Group Table | Opens the tool group table for managing grouped tools. |
| Tool Path Large | Switches toolpath panel to large view layout. |
| Tool Path Small | Switches toolpath panel to small view layout. |
| Tool Path View Bottom | Sets toolpath camera to bottom view. |
| Tool Path View ISO | Sets toolpath camera to isometric view. |
| Tool Path View Left | Sets toolpath camera to left view. |
| Tool Path View Right | Sets toolpath camera to right view. |
| Tool Path View Top | Sets toolpath camera to top view. |
| Transform: Array | Creates an array using the G-code part. Provides basic nesting function. |
| Transform: Mirror X | Mirrors toolpath across X axis. |
| Transform: Mirror Y | Mirrors toolpath across Y axis. |
| Transform: Rotate 180 | Rotates toolpath 180 degrees about the origin. |
| Transform: Rotate 90 CCW | Rotates toolpath 90 degrees counter‑clockwise. |
| Transform: Rotate 90 CW | Rotates toolpath 90 degrees clockwise. |
| UPS Power Off | Commands UPS‑coordinated shutdown of control power. |
| Zero All | Zeros all displayed work coordinates for X, Y, and Z. |
| Zero All Edit Offsets On/Off | Zeros all axes and toggles offset editing lock accordingly. |
| Zero X | Zeros X in the active work coordinate system. |
| Zero X Edit Offsets On/Off | Zeros X and toggles offset editing lock accordingly. |
| Zero Y | Zeros Y in the active work coordinate system. |
| Zero Y Edit Offsets On/Off | Zeros Y and toggles offset editing lock accordingly. |
| Zero Z | Zeros Z in the active work coordinate system. |
| Zero Z Edit Offsets On/Off | Zeros Z and toggles offset editing lock accordingly. |
Widgets
Widgets are small components that can be added to the dashboards to show data like the last probe position or to add buttons for controlling a chip conveyor. To see the list of available widgets right-click on the edge of a dashboard and select the drop down list.
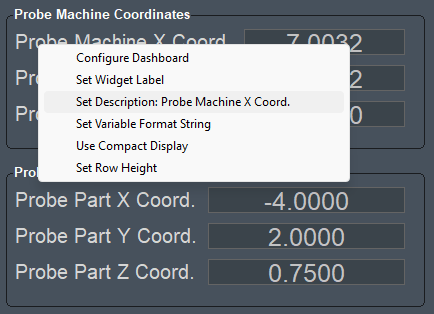
Many widgets have additional options to configure the way they look or which variables are shown in the widget. So see a list of options right-click inside the widget and select from the menu. The menu is context sensitive and some widgets have additional options, but these three options are always available.
|
Use compact display or specify height of the rows. The default is 22. Compact vs normal display
|
Select Get Info about the entry you right clicked |
If "Set Variable Format String" is an option, right-click on the row you want to change and select "Set Variable Format String." Then enter a string format with the following syntax: %.Xf (where the X represents how many decimal places. For example, if you only want 1 decimal place, enter %.1f. This will display a value 170.2353 as 170.2. You have to re-enter the value on the screen for it to display with the new format. Search for external documentation on operator (c-style string formatting) syntax for a complete list of options.
Many of the widgets allow you to add lists to be displayed: parameters, signals, variables, etc. If your options are displayed in a list, then you have several ways to select multiple values.
- You can add an individual item by selecting it, clicking the Add button at the bottom, and then the Close button.
- You can add a contiguous series of items. Select the first item, hold down the shift key on the keyboard and select the last item in the series. Click the Add button.
- You can repeat this action for other series of item, and click Add after each series is selected.
- You can add separate item. Select the first item. Hold down the control key on the keyboard and select each individual item that you want to add to the widget. Click the Add button.
- When you have finished adding all of the items, click the close button.
Set Widget Label allows you to rename that item to match usage on this system. Your system will be productive more quickly if you carry over the existing machine labeling to this MachMotion control interface.
All Inputs and All Outputs (Digital)
These are two separate widgets, one for digital inputs and one for digital outputs. They have the same function. They are useful for troubleshooting during installation, and it will display all the inputs or outputs (including ones not enabled or used) in a scroll-able window. Alternately, to just see particular I/O information, use these widgets:
- Analog Input and Output Signals (next entry down)
- Enabled Inputs and Outputs are at the hardware level
- Signals are at the software level and are mapped to particular hardware inputs and outputs
- I/O is a select-able list of both physical I/O and other system information.
|
If you add a description to an input in the Controls Inputs tab, that description will be used here. Note the scrollbar on the right side. All inputs are visible when you scroll. |
If you right click and select Run Test Sequence, you will see this popup. There are a large number of inputs and running the sequence 10 times will take some time. |
Analog Input and Output Signals
These are two separate widgets and each allows you to add specific analog input and output signals to your dashboard.
|
To add Analog signals, right click in the widget and select Add Variables.
|
Right click in the widget or directly on one of the signals.
|
Approach Distances
All axes will use this value when doing a probe move for both edges and corners. It is the maximum distance the probe will move while searching for material. If the probe is not activated before this distance is consumed, then an error will occur and the operation will be stopped.
| The Approach Distances widget is incorporated in the Fixtures Tab, and is best used there. |
Axis Compensation
| This is used on grinders to adjust for the grind wheel size changing during dressing or grind cycles. Grinder controls will have these functions configured in their profile, and you will not normally need to add this widget. Refer to the appropriate manual for your type of grinder, and search for compensation. |
Calculator
| This is a simple calculator that is useful if you often need one while working on the control. There are no special features to configure here. If you need a calculator with more advanced features, the Windows calculator is available. |
Current Fixture Offsets
This displays the current offset of each axis from the machine zero location on that axis. It is the same as the opening the Fixtures Offsets table on the Fixtures tab. This is a display widget. If you want to change these values, open the Fixture Offsets table on the fixtures tab.
Cylindrical Grinder Part Offsets
This is used for Cylindrical grinders. The part offset table (Part Correction Offset) which, when multiple features are being ground on the part, can be used in conjunction with an "E" variable in the program to allow adjustments to each feature individually.
DRO Measure
| This provides a digital "tape measure" that can measure axis movement, and be reset at will. It does not change any operating values or parameters. |
Dual Table
| This widget is used on routers with two tables. Setup and use is documented in the 2000 Series Dual Table article. |
Enabled Inputs and Outputs
| These widgets will show only the inputs or outputs that been enabled. Right clicking on the display will bring up a menu. If you click on a particular input or output, you can get information about that entry. |
Feedback
|
|
This provides an on-screen indicator when any of the axes are moving. You select the axes that you want to monitor. |
|
Right click on the border space around the buttons and select Configure Widget to access the display options.
The Grid Configuration, at the top, determines how many rows and columns of axis indicators you will have. |
File Travel Limits
| This displays the extents of movement you will have on each axis for the file that is loaded. Using this along with the yellow soft limit display on the tool path will help you identify fixture problems before you run a file. |
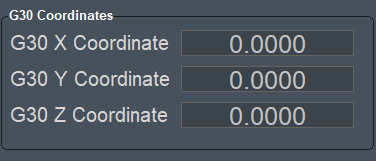
G30 Coordinates
| This is similar to the G28 command. G28 ends at machine zero while G30 allows you to specify different end coordinates than machine zero. |
G54 - G59 fixture Offsets
|
This widget displays the current values of your offsets in individual windows for each offset. You may add a widget for each set of offsets that you want to monitor. If you want to change these values, open the Fixture Offsets table on the fixtures tab. If you only need a single widget that dynamically updates to show the current offsets, use the Current Fixture Offsets (above). The Fixtures Tab on the control also provides easy access to the most used fixture features. |
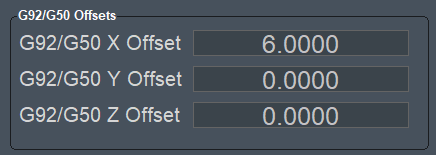
G92/G50 Offsets
Most operators will use G54–G59 fixture offsets or GOTO positions instead of G92 and G50/G52, which were used before fixture offsets existed. Try these features first. You may also use the Head Shift Offset and Work Shift Offset widgets to make adjustments directly on the screen - without any G-Code changes. The Fixtures Tab on the control also provides easy access to the most used fixture features.
There are cases where G92 and G52 are very useful, and for that you need to refer to the full documentation links above.
|
The widget will display any offsets created with G92 or G52 in your G-Code.
|
You may also change the labels of the offsets to match your naming convention. |
Head Shift and Work Shift Offsets
Head Shift and Work Shift offsets are very similar.
- Head shift is used for permanent offsets related to multiple heads - such as a router with a standard spindle, and a drill bank, or an engraving laser. You need to shift your your cut path to use the other tool while maintaining the same fixture coordinates.
- Work shifts are used for temporary changes. Your stock may have a defect and you need to shift your fixture coordinates by 0.005 inches for this piece. This widget provides an easy way to make those kind of temporary adjustments quickly, without changing your existing fixture offsets. When you are done with this piece you can reset the work offsets to 0.0000 and use unmodified fixture offsets.
The values entered in the on-screen widget update the fixture table for the head or work shift, but they do not change your current fixture offsets (G54, G55, etc). You change the head shift values in the widget, or directly in the Fixture Offsets Table.
The head and work shift values will reset to zero when you restart the software. If you want to set permanent values for the shifts, you can change that option in the MachMotion Plugin. Your options are:
- Reset to Zero
- Restore the last value you entered
- Restore a permanent value
Head and work shift values will not change the standard G54-G59 work offsets, but they do stack on top of those values. You can also have both head shift and work shift values in effect at the same time. The head and work shift values will apply to your current work offsets.
I/O
This is used for diagnostics during system setup, and shows the electrical status of the input and output ports on the main control panel, and diagnostic information about multiple other aspects of the system. See Signals below.
These examples show how the I/O indicators change when the Goto and MDI features are used.
|
|
||||
IVIS
This is the interface for a software tool used on some grinders. If your system uses IVIS, we will configure this widget for you.
Job File
This widget is used in custom profiles. Please contact MachMotion for configuration.
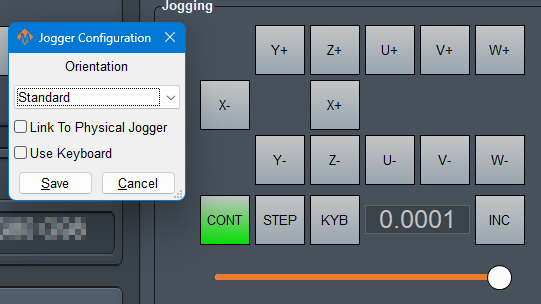
Jogging
This widget provides both on-screen and keyboard jogging. There are different on-screen axis button configurations to match your system.
|
|
|
|
Lite is used to select the axis on computers that have physical + and - jog buttons on the panel. |
- CONT is continuous movement as long as you press the relevant axis button.
- STEP moves the axis by one increment with each press of the axis button.
- KYB uses keyboard mappings to control different aspects of the jogging function. Select the functions you want to use in the Jogger Configuration window, then map the key combinations in the Keyboard Inputs plugin.
- INC cycles through the jogging distance increments: 0.0001, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1.0
The Jogger Configuration option to link to the physical jogger, allows you to keep the feedrate value synced with other physical pendants.
This is the feedrate slider
|
Opening the Keyboard Plugin to map keys
|
Last Commanded Coordinates
This reports the last position that each axis has been commanded, either by the G-Code file or by MDI.
G0 X1 Y1 Z1
G0 X2 Y2These G-Codes above resulted in this display. If an axis is not commanded for multiple blocks of code, it will retain the last commanded coordinate.
Mach Parameters
These are the values stored in profile\parameters.ini and are best accessed in the MachMotion Plugin. Pull down the Configure menu | Plugins -> MachMotion parameters. Normally you will not need to monitor or change these values. This widget is primarily used for system customization.
|
|
Right-click in the widget to bring up the menu. This menu is specific to #5130 because I right-clicked that entry.
Machine Coordinates
These are the distances from the machine zero on each axis. You can toggle the DRO to show View Machine, and you can use this widget to display machine values at all times. See also Part Coordinates.
Notepad
This is a simple notepad that retains the text even when the control is fully power cycled. Right-clicking will display the options.
Original Offsets
Please refer to, and use, the Current Fixture Offset widget
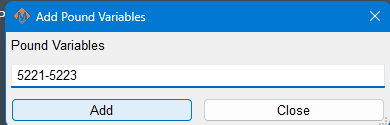
Pound Variables
The system variables, or pound variables (# variables) are documented in the Macro B Reference Guide in the System Variables section. They are shared memory between G-Code files, and M-Codes and plugins.
|
From the Macro B section 3.6 System Variables
|
Setting the widget values |
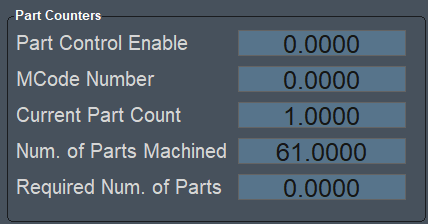
Part Counters
This widget is incorporated into the standard interface, on the GCode tab, and it is best used there.
|
|
Part Counters (internal documentation)
Probe Machine Coordinates and Part Coordinates
Registers
Registers are documented in 4 Registers as part of the core Mach documentation. This widget allows you to display particular registers and their values. You can also browse the entire tree from the main menu. Pull down Diagnostic | Regfile
|
|
Scheduler
This widget is used to customize system operation when a customer's work flow requires it. If you need this functionality, please contact MachMotion support and request a quote for custom configuration.
|
|
Opening the Scheduler will open a new window with the Schedule Editor. The Load button will open a file browser to select the job files you want to schedule. Once the jobs are listed, you can reorder them, and change the quantity of times to run a particular job.
Signals
Also see I/O and the mapping documentation for your motion controller. The signals are mapped to particular input and output ports. In this example, the underlying I/O ports are connected, and the signals have been mapped to report I/O status to the system.
Subspindle Control
|
This widget is used to set the speed and start the spindle. Configuration details and examples are located in these bookstack articles:
|
Tool Wear Offsets
Please enter your tool wear offsets in the Tool Table, or using G10: Fixture and Tool Offset Setting. Refer to the Cutter Compensation portion of the Mach4 G-Code and M-Code Reference for the concepts in cutter compensation.