2000 Series Centerless Grinder Operating Manual
Introduction
This manual is designed to give the operator a working understanding of how to operate your new CNC Centerless Grinder. The control is designed to simplify the operation of your Centerless Grinders high-end features. We have elected not to use g-codes to manipulate the servo axis. Instead, we use the combination of a simplified data entry routine with a graphic interface that the operator will find extremely easy to use.
Each page contains items that are used specifically for the function of the individual screen like starting and stopping motors, changing cycle modes, entering new feedrates and positions, etc.
There are other items that are used globally. This means that the same items are found on all of the pages. Primarily they are the machine state, cycle time, and date and time at the top of the screen, the axis position, cycle status, current feedrate, and wheel speed on the right side of the screen.
Operator Panel Overview
The following is a description of the Operator Panel and it's functional devices. The numbered balloons point to the object.
- Computer HMI. Consists of screens designed to control the machine functions and feedback information on the machine state.
- Emergency Stop Button. Used to stop process and motors in the event of an emergency, by turning off all active output logic.
- Cycle Start Button. Used to initiate an automatic cycle and confirm actions.
- Feedhold Button. Used to pause an automatic cycle in place.
- Cycle Stop Button. Used to stop an automatic cycle in place.
- Reset Button. Used to clear or reset machine faults and enable system servo motors.
- Rapid Speed Control Buttons. Used to change the speed the machine moves during rapid moves.
- Feedrate Override Knob. Used to change the speed the machine moves during feed moves.
- Spindle Control Buttons. Used to start and stop the wheel and change the speed override value.
- Programmable Function Buttons. Used to customize the control.
- Jog Control Buttons. Used to manually jog servo axes while the machine is not in a cycle.
- Jog Speed Knob. Used to control the speed during manual jog moves.
Control Overview
The control supports an In-Feed cycle for plunge grinding and a Thru-Feed cycle for bar grinding. It also supports Grind Wheel and Regulating Wheel Dressing (Truing) with up to 2 coordinated axes each.
Screen Navigation
- Status
- Status - Displays any current messages (Home All Pressed, Cycle Start Pressed, etc.)
- State - Displays the current state of the machine (Run, Feed Hold, etc)
- Cycle Time - Displays how long the GCode has been running
- Date - Date and time of the timezone of the control
- Operation Pages
- Operation Display
- Axis Position Display
- Cycle Status
- Feedrate Display
- Grind Wheel Display
- Regulating Wheel Display
- Grinder Dashboard
- Configurable Dashboard with Widgets for machine auxiliaries (Hydraulics, Mist Collectors etc.)
- Side Bar Dashboard
- Configurable Dashboard with Widgets for productivity
In-Feed Cycle
The In-Feed Grinding cycle begins at the Load Position and rapids to the start of the Coarse grind and continues through Medium and Fine with optional Feedrates and pauses until it reaches the Finish Position and pauses to spark-out. Then rapids to the Retract Position and completes the cycle at the Load Position.

In-Feed Cycle Parameters
Position Parameters
- Retract Position: The position the slide will move to at the end of the cycle to drop or eject the part. When the Retract Position is not needed set the make it equal the Load Position.
- Load Position: This is the first and last slide position in the cycle.
- Finish Position: This is the final grind position and the position that Fine, Medium and Coarse grind amounts are referenced from. The Finish Position can be set to a diameter or 0 depending on the setup.
Cycle Parameters
- Coarse Grind
- Coarse Grind Amount: The amount to be removed at the Coarse Feedrate
- Coarse Feedrate: The Feedrate used during Coarse grind
- T1: Optional Delay at the end of the Coarse grind
- Medium Grind
- Medium Grind Amount: The amount to be removed at the Medium Feedrate
- Medium Feedrate: The Feedrate used during Medium grind
- T2: Optional Delay at the end of the Medium grind
- Fine Grind
- Fine Grind Amount: The amount to be removed at the Fine Feedrate
- Fine Feedrate: The Feedrate used during Fine grind
- T3: Optional Delay at the end of the Fine grind, sometimes referred to as Sparkout Time
- Retract Delay
- T4: Optional Delay at the Retract position to allow the part to drop between the Regulating Wheel and Grinding Wheel
- Load Delay
- T5: Optional Delay at the end of the cycle. This is normally used along with Cycle Repeat to allow time to load the next part.
In-Feed Comp
Comp is used to adjust the part diameter. For more info see Compensation.
For info on Grind Position calibration see Grind Position Calibration
At any point Cycle Stop or Retract buttons will cause the slide to Rapid to the Retract Position.
Thru-Feed Cycle
Thru-Feed Grinding will rapid the slide to the Grind Position and stay there.
Thru-Feed Cycle Position Parameters
- Retract Position: The position the slide will move to when Cycle Stop or Retract are used.
- Finish Position: This is the position the slide will move to when the cycle is ran.
Thru-Feed Comp
When the slide is at the Grind Position and Comp offset is applied the slide will move back to the Grind Position. When the slide is at any other position than the Grind Position the slide will apply the offset without any movement. For more info see Compensation.
For info on Grind Position calibration see Grind Position Calibration
At any point Cycle Stop or Retract buttons will cause the slide to Rapid to the Retract Position.
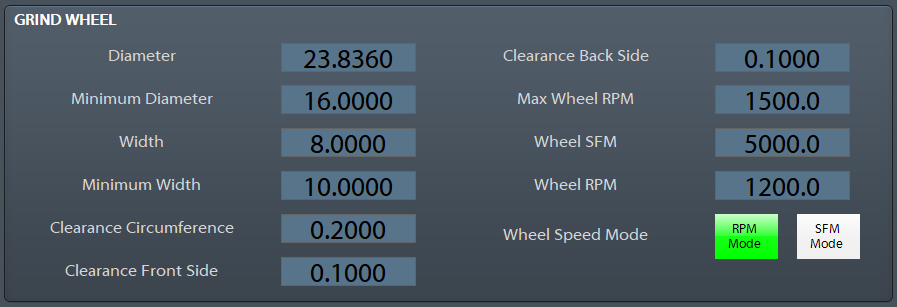
Grind Wheel
The Grind Wheel Page is where the Grind Wheel parameters and dress parameters are configured. Depending on the enabled options of the machine some of these parameters will be hidden.
Use the following figure for Grind Wheel dimensions and clearances

Grind Wheel Parameter Descriptions
- Diameter: The current wheel diameter. The dressing cycle automatically updates the wheel diameter. When a new wheel is mounted on the machine this parameter should be updated.
- Minimum Diameter: When the wheel is dressed to this diameter the control will not allow any more dress cycles to complete. The operator will get a alarm messages stating that the wheel is to small.
- Width: The current width of the wheel, used in the straight dressing cycles.
- Minimum Width: When the wheel is side dressed to this width the control will not allow any more dress cycles to complete. The operator will get a alarm messages stating that the wheel is to narrow.
- Clearance Circumference: This is used in the dress cycle, the diamond will rapid to this clearance position and then switch to a feedrate move before touching the wheel.
- Clearance Front Side: This is used in the dress cycle, the diamond will rapid to this clearance position and then switch to a feedrate move before touching the wheel.
- Clearance Back Side: This is used in the dress cycle, the diamond will rapid to this clearance position and then switch to a feedrate move before touching the wheel.
- Max Wheel RPM: Max RPM the wheel can be commanded to run. Check the wheel specs and keep this number under it.
- Wheel SFM: The commanded Surface Feet Per Minute or (SFM). There are buttons just below that set the mode, RPM Mode or SFM Mode.
- Wheel RPM: The commanded Rotations Per Minute or (RPM). There are buttons just below that set the mode, RPM Mode or SFM Mode.
- Wheel Speed Mode: RPM Mode or SFM Mode switch the command source between Wheel RPM and Wheel SFM modes.
Grind Wheel Diamond Setup
- Using the Jog buttons or MPG, Jog the GD (X) axis so the diamond is just touching the front side of the wheel.

- Press the yellow Teach button for X.
- Using the Jog buttons or MPG, Jog the GD (Y) axis so the diamond is just touching the circumference of the wheel.

-
Press the yellow Teach button for Y.
Y Diamond Comp
Diamond Comp can be used at anytime and during a dress cycle to move the diamond in closer to the wheel. Sometimes the wheel will wears a lot between dress cycles, and this can be use to reduce the number of dress passes. For more information see Compensation.
Dress Cycles
The control supports two dress cycles for the wheels, Standard Dress and New Wheel Dress. Both of these cycles are very similar and allow you to store two sets of parameters, one for normal production (Standard Dressing) and one set of parameters for shaping a wheel (New Wheel Dress).
Use the following table to compare the dress cycles:
| Dress Cycle Features | Standard Dress | New Wheel Dress |
| Dress Rate | Yes |
Yes |
| Dress Passes | Yes |
Yes |
| Dress Amount | Yes |
Yes |
| Spark-Out Passes (Free Passes) | Yes |
No |
| Changing the profile of the wheel | No | Yes |
Standard Dress
The Standard Dress is the default dress cycle and would be used after the wheel has been shaped and is ready for production. Standard Dress will use whatever profile was selected on the New Wheel Dress page.
Standard Dress Parameters
- Dress Rate: The feedrate the diamond will travel across the wheel.
- Dress Passes: The number of passes the diamond will make across the wheel.
- Dress Amount: The amount mount of wheel to remove per pass. The amount is in radius of the wheel so 0.001 will change the wheel diameter by 0.002.
- Spark-Out Rate: The feedrate the diamond will travel across the wheel during the Spark-Out Pass or Free Pass.
- Spark-Out Passes: The number of passes the diamond will make across the wheel without in-feeding the diamond into the wheel. Sometimes this type of pass is called a Free Pass.
- In-Feed Parts Per Pass: This is only used in the In-Feed Cycle and will cause the control to automatically call a dress cycle after the number of cycles is greater than the value in this parameter. A value of 0 disables this feature.
You can change the amount the dress cycle comps the infeed by adjusting the Comp Dress Factor under Service->Grind Settings.
A setting of 0 will disable the comp completely. This is used when you have a diamond grind wheel. A setting of 1 will comp the exact amount you dress (dress amount x dress passes = total comp on the infeed.
New Wheel Dress
The New Wheel Dress is the cycle used to create the profile in the wheel and to rough the wheel into shape.
New Wheel Dress Parameters
- Dress Rate: The feedrate the diamond will travel across the wheel.
- Dress Passes: The number of passes the diamond will make across the wheel.
- Dress Amount: The amount mount of wheel to remove per pass. The amount is in radius of the wheel so 0.001 will change the wheel diameter by 0.002.
- Custom Profile: When the Custom Profile is off the dress profile will be a straight profile and use the Grind Wheel Parameters to make the profile. When Custom Profile is on there will be a subroutine with a profile that the diamond will follow.
Wheel Profiles
The control supports Straight Profile and Custom Profile. The straight profile uses the data from the Grind Wheel Parameters and the custom profile uses the Grind Wheel Profile Dressing dialog to draw any custom profile. To switch between the straight and custom profiles turn the Custom Profile on or off.
New Wheel Dress - Straight Profile
When the Custom Profile is off the dress profile will be a straight profile and use the Grind Wheel Parameters to make the profile.
New Wheel Dress - Custom Profile
When the Custom Profile is on the the dress cycle will use the Subroutine that is created with the profile number.
Custom Profile
Profile Number shows the selected Profile to use. To change the profile press Open.
There are 3 buttons for creating opening and editing the custom profiles.
- New will open the Grind Wheel Profile Dressing dialog with blank profile.
- Open will open a File Browser dialog and allow you to select a profile.
- Edit will open the current profile in the Grind Wheel Profile Dressing dialog.
Grind Wheel Profile Dressing
The Grind Wheel Profile Dressing is where you create your custom dress profile for the wheel. The profile can be a mixture of lines and arcs. There are four columns Type, X Position, Y Position and Radius showing the data for the given line or arc segment. The example below has profile number 2005 loaded.

Add Line Segment
Remove Line Segment
Use the Remove button to remove any line segment.
Profile Operations
Open: Open a different dress profile
Add: Add new line segment to the dress profile
Remove: Remove a line segment from the dress profile
Save As: Save the profile with a new name
Save: Save the current profile
Regulating Wheel
The Regulating Wheel Page is where the Regulating Wheel parameters and dress parameters are configured. Depending on the enabled options of the machine some of these parameters will be hidden.
Use the following figure for Regulating Wheel dimensions and clearances

Regulating Wheel Parameter Descriptions
- Diameter: The current wheel diameter. The dressing cycle automatically updates the wheel diameter. When a new wheel is mounted on the machine this parameter should be updated.
- Minimum Diameter: When the wheel is dressed to this diameter the control will not allow any more dress cycles to complete. The operator will get a alarm messages stating that the wheel is to small.
- Width: The current width of the wheel, used in the straight dressing cycles.
- Minimum Width: When the wheel is side dressed to this width the control will not allow any more dress cycles to complete. The operator will get a alarm messages stating that the wheel is to narrow.
- Clearance Circumference: This is used in the dress cycle, the diamond will rapid to this clearance position and then switch to a feedrate move before touching the wheel.
- Clearance Front Side: This is used in the dress cycle, the diamond will rapid to this clearance position and then switch to a feedrate move before touching the wheel.
- Clearance Back Side: This is used in the dress cycle, the diamond will rapid to this clearance position and then switch to a feedrate move before touching the wheel.
- Max Wheel RPM: Max RPM the wheel can be commanded to run. Check the wheel specs and keep this number under it.
- Wheel SFM: The commanded Surface Feet Per Minute or (SFM). There are buttons just below that set the mode, RPM Mode or SFM Mode.
- Wheel RPM: The commanded Rotations Per Minute or (RPM). There are buttons just below that set the mode, RPM Mode or SFM Mode.
- Wheel Speed Mode: RPM Mode or SFM Mode switch the command source between Wheel RPM and Wheel SFM modes.
Regulating Wheel Diamond Setup
Dress Cycles
The control supports two dress cycles for the wheels, Standard Dress and New Wheel Dress. Both of these cycles are very similar and allow you to store two sets of parameters, one for normal production (Standard Dressing) and one set of parameters for shaping a wheel (New Wheel Dress).
Use the following table to compare the dress cycles:
| Dress Cycle Features | Standard Dress | New Wheel Dress |
| Dress Rate | Yes |
Yes |
| Dress Passes | Yes |
Yes |
| Dress Amount | Yes |
Yes |
| Spark-Out Passes (Free Passes) | Yes |
No |
| Changing the profile of the wheel | No | Yes |
Standard Dress
The Standard Dress is the default dress cycle and would be used after the wheel has been shaped and is ready for production. Standard Dress will use whatever profile was selected on the New Wheel Dress page.
Standard Dress Parameters
- Dress Rate: The feedrate the diamond will travel across the wheel.
- Dress Passes: The number of passes the diamond will make across the wheel.
- Dress Amount: The amount mount of wheel to remove per pass. The amount is in radius of the wheel so 0.001 will change the wheel diameter by 0.002.
- Spark-Out Rate: The feedrate the diamond will travel across the wheel during the Spark-Out Pass or Free Pass.
- Spark-Out Passes: The number of passes the diamond will make across the wheel without in-feeding the diamond into the wheel. Sometimes this type of pass is called a Free Pass.
- In-Feed Parts Per Pass: This is only used in the In-Feed Cycle and will cause the control to automatically call a dress cycle after the number of cycles is greater than the value in this parameter. A value of 0 disables this feature.
New Wheel Dress
The New Wheel Dress is the cycle used to create the profile in the wheel and to rough the wheel into shape.
New Wheel Dress Parameters
- Dress Rate: The feedrate the diamond will travel across the wheel.
- Dress Passes: The number of passes the diamond will make across the wheel.
- Dress Amount: The amount mount of wheel to remove per pass. The amount is in radius of the wheel so 0.001 will change the wheel diameter by 0.002.
- Custom Profile: When the Custom Profile is off the dress profile will be a straight profile and use the Regulating Wheel Parameters to make the profile. When Custom Profile is on there will be a subroutine with a profile that the diamond will follow.
Wheel Profiles
The control supports Straight Profile and Custom Profile. The straight profile uses the data from the Regulating Wheel Parameters and the custom profile uses the Regulating Wheel Profile Dressing dialog to draw any custom profile. To switch between the straight and custom profiles turn the Custom Profile on or off.
New Wheel Dress - Straight Profile
When the Custom Profile is off the dress profile will be a straight profile and use the Regulating Wheel Parameters to make the profile.
New Wheel Dress - Custom Profile
When the Custom Profile is on the the dress cycle will use the Subroutine that is created with the profile number.
Custom Profile
Profile Number shows the selected Profile to use. To change the profile press Open.
There are 3 buttons for creating opening and editing the custom profiles.
- New will open the Regulating Wheel Profile Dressing dialog with blank profile.
- Open will open a File Browser dialog and allow you to select a profile.
- Edit will open the current profile in the Regulating Wheel Profile Dressing dialog.
Regulating Wheel Profile Dressing
The Regulating Wheel Profile Dressing is where you create your custom dress profile for the wheel. There are four columns Type, Z Position and A Position showing the data for the given line segment. The example below has profile number 3010 loaded.
Add Line Segment
Remove Line Segment
Use the Remove button to remove any line segment.
Profile Operations
Open: Open a different dress profile
Add: Add new line segment to the dress profile
Remove: Remove a line segment from the dress profile
Save As: Save the profile with a new name
Save: Save the current profile
Operations
Running Grinding Cycle
Before running parts on the control, be sure the following steps have happened after starting the control software:
- Machine is homed.
- Part setup is complete.
- The Grind Position has been calibrated.
- The In-Feed Cycle Parameters or Thru-Feed Cycle Position Parameters cycle parameters are set.
- Starting the cycle:
- In-Feed Cycle: Press "Cycle Start" while the In-Feed page is active.
- Thru-Feed Cycle: Press "Cycle Start" while the Thru-Feed page is active.
Dressing the Wheels
Before dressing the wheels, be sure the following steps are complete:
- Machine is homed.
- Mount the wheels on their respective spindles.
- Set the regulating wheel to the proper angel.
- Follow the Grind Wheel Diamond Setup and the Regulating Wheel Diamond Setup.
- Configure the dressing profiles for both the Grind Wheel and Regulating Wheel
- Starting the cycle:
Appendix
Start-Up Sequence
- Apply power to the control
- Press the Reset button on the operator panel. The control will go through it's start-up sequence. Allow time for the computer to start up.
- Start the Mach4 application from the shortcut on the desktop. Allow time for the system to initialize.
- Press Cycle Start when the control requests to Enable and Home the servo axes.
Homing Machine
Most machines are configured with a Enable and Home dialog that will be shown on startup.
Press the Cycle Start button on the dialog or the Cycle Start button on the operator panel. The machine will enable the servos and home to the switches.
If for some reason this dialog is not shown you can manual enable the machine by pressing Reset and then navigate to the Service page.
Home each axis individually or press Home All to home all axes.
Part Setup
Part Setup can very from machine to machine, so this is a very general outline to part setup. The following drawing is a setup with the work height above centerline.
A Centerless grinder has three main components: a grinding wheel, a regulating wheel and a workblade.
- Select the blade of proper material, thickness and top angle.
- Clamp the workblade with the correct relationship of the part center height above the wheel’s centerline.
- Clamp the workrest to the lower slide.
- Mount the wheels on their respective spindles.
- Set the regulating wheel to the proper angel.
- Dress Regulating Wheel
- Dress Grinding Wheel
- Select the proper regulating wheel speed.
- Set the regulating wheel distance to the workblade.
- Entrance/exit guide alignment.
Grind Position Calibration
Part Calibration should be done after the Part Setup steps have been complete.
Calibration
- Place a part on the Workblade and if needed start the Regulating Wheel and Grind Wheel.
- Using the Jog buttons or MPG, Jog the slide in so the part is just touching the Grind Wheel.
- Press the grey Edit Offsets button. When this is active the Edit Offsets button will change to yellow.

- When Edit Mode is active the Position DROs will be editable and there will be Zero buttons next to the DROs.

- Press the Zero button or click into the DRO and Input the desired position and press Enter.

- Press the yellow Edit Offsets button to lock the offsets.
Now the Grind Position should be calibrated.
Use Compensation to make small adjustments to the Grind Position
Compensation
Compensation or Comp is used to adjust the slide offsets to maintain the part diameter as the wheel breaks down and wears. It can also be used to adjust the diamonds closer to the wheel while dressing. Comp acts differently depending on the grinding mode. See the table below to see how Comp is applied.
| Grinding Mode | Adjust slide offsets? | Moves to position after adjustment? |
| In-Feed Grinding | Yes |
No |
| Thru-Feed Grinding at Grind Position | Yes | Yes |
| Thru-Feed Grinding not at Grind Position | Yes | No |
There are Comp buttons on the screen, and some machines have buttons on panels for applying Comp. Coarse and Fine Comp buttons allow the operator to choose between two defined increment sizes.
Total Comp
Total Comp is for the operator to track how much Comp as been applied. Resting the Total Comp will only zero the Total Comp indicator.
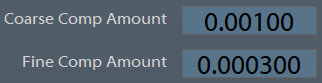
Configure Comp Amount
Coarse and Fine Comp amounts are configurable on the Service / Grinder Settings page.
Backlash Move
When Comp is being applied and the slide is moving away from the grinding wheel the control can make an extra move to take up any loss of motion from backlash in the slide. To enable this option open the Interface Config dialog from the Service page and search for Backlash. Modify the following parameters.
- Backlash Move Enabled: This enables and disables the Backlash move
- Backlash Move Distance: This is the distance the slide will move when applying Comp
MDI Programmed Movement
To command a movement using the MDI feature, press the [MDI] button.
I/O Part Loader
Part Loader Parameters
| Parameter Name | Description |
Required |
| Enabled | Enables or disables the loader function | No |
| Type | Method I/O, PLC Sequence, Subroutine | No |
| Unload On End Of Cycle | No | |
| Load Request Output | Output | Yes |
| Load Request Confirm Input | Input | No |
| Load Complete Input | Input | Yes or In-Cycle Input |
| Load Complete Confirm Output | Output | No |
| Unload And Load Request Output | Output | Yes |
| Unload And Load Request Confirm Input | Input | No |
| Unload And Load Complete Input | Input | Yes or In-Cycle Input |
| Unload And Load Complete Confirm Output | Output | No |
| Unload Request Output | Output | Yes |
| Unload Request Confirm Input | Input | No |
| Unload Complete Input | Input | Yes or In-Cycle Input |
| Unload Complete Confirm Output | Output | No |
| Wheels In Position Output | On when wheels are at the load position |
Yes |
| In-Cycle Input | Should be on while the loader is in cycle |
No |
| Alarm Input | Creates Alarm and opens dialog | No |
| Empty Input | Creates Information dialog | No |
Load Part Diagram

Unload Part Diagram

Part Loader Alarm
The Part Loader has a parameter named "Part Loader Alarm Input" that can be mapped to an input signal or IO and when the input goes high an Alarm will be generated.
It also supports a OEM Parameter Register named "Part Loader Alarm Message Register" that is used as a mapping register that holds the path to a register that will hold the alarm code. The loader would need to write the alarm code to the register to be displayed.
There is also a register named "Part Loader Alarm Messages" that can hold messages in CSV format and show custom string messages based on the number written to the "Part Loader Alarm Message Register". If this is setup the Alarm message will include the messages from the parameter.
Example of the CSV string for parameter "Part Loader Alarm Messages"
100,Alarm Message 100
101,Alarm Message 101
102,Alarm Message 102
103,Alarm Message 103Subroutine Part Loader
O701 (Unload And Load Part)
O702 (Load Part)
O703 (UnLoad Part)
O704 (Eject Part at Retract Position)
O710 (Part Loader Retract Cycle)
These are the subroutines that need to be created and modified for every machine. They should be placed in the "C:\Mach4\Subroutines" directory.
O701
(Unload and Load Part)
(Often these will need to be customized from one machine to another. We normally move them to the root Mach4 directory under Subroutines)
M99
%
O702
(Load Part)
(Often these will need to be customized from one machine to another. We normally move them to the root Mach4 directory under Subroutines)
M99
%
O703
(Unload Part)
(Often these will need to be customized from one machine to another. We normally move them to the root Mach4 directory under Subroutines)
M99
%
O710
(Part Loader Retract Cycle)
(Often these will need to be customized from one machine to another. We normally move them to the root Mach4 directory under Subroutines)
M99
%Part Kicker
Part Kickers are used to kick the part out of the machine during the retract cycle. There is a interlock that should make the retract cycle wait on the park kicker if its still in cycle.
Global Parameters
- Part Kicker Enabled
- Retract Percent
I/O Part Kicker
Parameters
- Part Kicker Input (Optional)
- Part Kicker Output
- Part Kicker Output On Time (ms)
OB Axis Part Kicker
Parameters
- Part Kicker Type OB Axis
- Part Kicker OB Axis ID
- Part Kicker OB Axis Feedrate
Pound Variables for positions
- #9067 - Part Kicker OB Axis Home Position
- #9068 - Part Kicker OB Axis Load Position
- #9069 - Part Kicker OB Axis Extend Position
Warranty Information
MachMotion warranty policy is subject to change. Updated information is available at our website:
https://machmotion.com/warranty
The MachMotion Team
http://www.machmotion.com
14518 County Road 7240, Newburg, MO 65550
(573) 368-7399 • Fax (573) 341-2672